The Secret Language of Search Engines: A Guide to Using a Schema Markup Generator to Unlock Rich Snippets
Imagine your website trying to explain itself to a super-intelligent robot. You’ve got beautiful content, insightful articles, and amazing products, but the robot sees it all as just text and images. How do you make sure it truly understands that your business is a local bakery, your article is a step-by-step guide, or your product has five-star reviews?
The answer lies in schema markup, a powerful, hidden language that gives context to your content. And if the idea of coding this "secret language" sounds daunting, don't worry. This comprehensive Guide to Using a Schema Markup Generator is your roadmap to effortlessly speaking Google's language and unlocking those coveted rich snippets that make your website stand out in search results.
You’re about to discover how a simple online tool can transform your website’s visibility, attract more clicks, and future-proof your SEO strategy in an AI-driven world.
At a Glance: What You'll Learn
- What Schema Markup Is (and Isn't): A quick, clear explanation of structured data and its purpose.
- Why It's Critical for SEO: How schema boosts visibility, improves search engine understanding, and fuels rich snippets.
- The Power of a Generator: How these tools simplify complex coding and make schema accessible to everyone.
- Key Schema Types: The most common categories to identify and mark up your content.
- Step-by-Step Implementation: A practical walkthrough from choosing a generator to validating your code.
- Advanced Tips & Pitfalls: Strategies for mastering schema and avoiding common mistakes.
- Monitoring Success: How to track your rich snippet performance.
Why Your Website Needs to Speak "Schema": The Power of Structured Data
Think of the internet as a massive library. Your website is a book within that library. Without schema markup, your book might have a nice cover and clear content, but the library catalog system (search engines like Google, Bing, Yahoo!, and Yandex) struggles to categorize it precisely. Is it a recipe book, a travel guide, a biography, or a technical manual?
Schema markup, often called structured data, is like adding a highly detailed, universally understood index card to your book. It’s a specific vocabulary—defined by Schema.org, a collaborative initiative by the big search engines—that you embed into your website’s HTML. This markup provides explicit, unambiguous context to search engine crawlers and AI systems about the meaning behind your content. It tells them: "This isn't just a string of text; this is a product's price. This isn't just a picture; this is the author's headshot. This isn't just a date; this is an event's start time."
This optimization doesn't change how your page looks to human visitors. Instead, it radically enhances machine interpretation, primarily using a format called JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data), which Google officially prefers.
Here’s why embracing schema isn't just an option; it's a strategic imperative for any website owner:
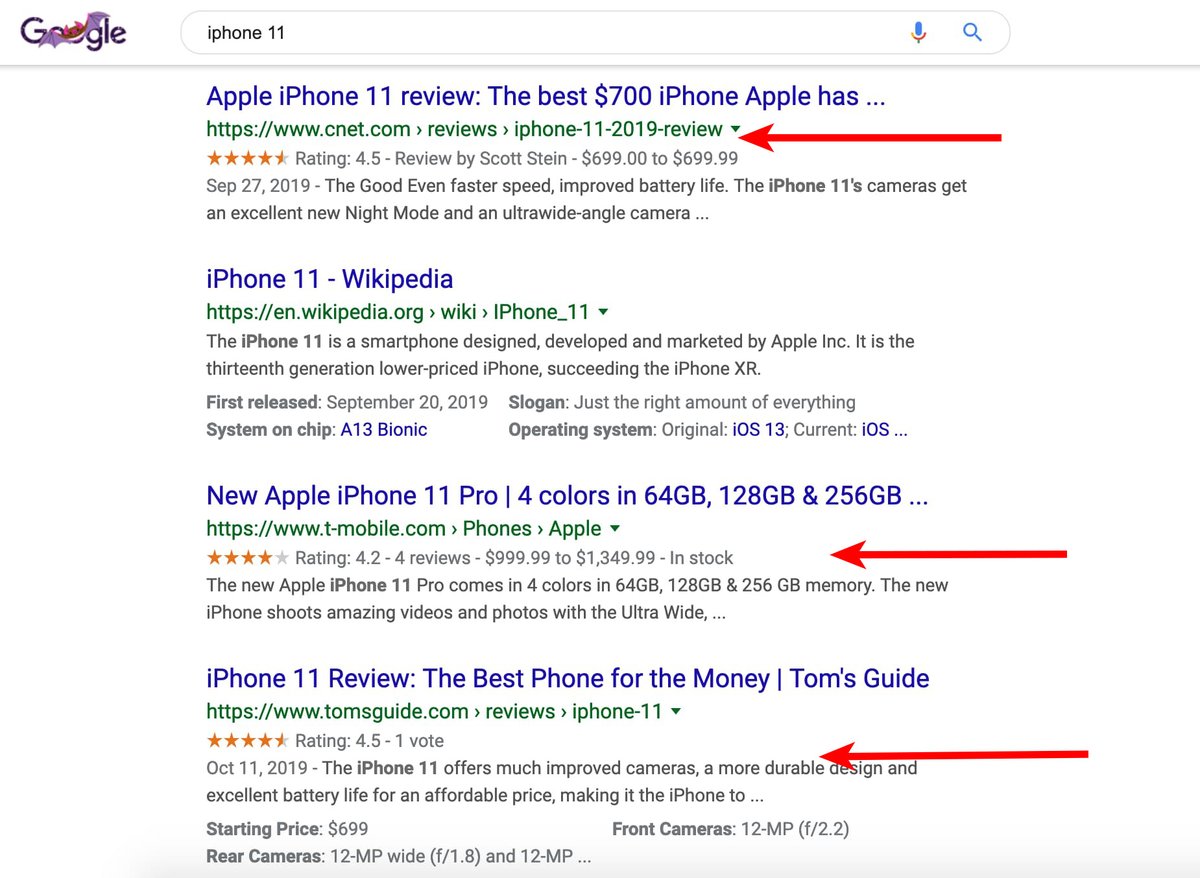
- Unlocking Rich Snippets & Enhanced SERP Visibility: This is the most visible benefit. Schema markup allows your pages to appear in search results with "rich snippets"—extra, eye-catching details like star ratings, product prices, event dates, recipe cook times, or FAQ toggles. These visual enhancements make your listing stand out dramatically from plain blue links, leading to a significant increase in click-through rates (CTR) by 20-30% or even more. More clicks mean more traffic, which is the lifeblood of any online presence.
- Improved Search Engine & AI Understanding: Beyond rich snippets, schema provides critical context for accurate indexing and ranking. As search engines evolve and AI-powered systems (like Google AI Overviews, ChatGPT, and Perplexity) become central to information retrieval, structured data is their primary language for truly understanding your content. It makes your information more likely to be summarized, cited, and used to answer complex queries.
- Better Voice Search Performance: Voice assistants (think Alexa, Siri, Google Assistant) rely heavily on structured data to provide direct, concise answers to user queries. If your content is clearly marked up, it significantly increases its chances of being chosen as the definitive answer for voice search.
- Future-Proofing Your SEO Strategy: The trend is clear: structured data will only grow in importance as search engines become more sophisticated and AI-driven. Investing in schema now ensures your website remains competitive and relevant in the evolving digital landscape.
- Gaining a Competitive Advantage: While schema adoption is growing, it's still not universally implemented to its full potential. Effective schema differentiates your website, making it more visible and more appealing than competitors who neglect this powerful tool.
Demystifying the Generator: What It Does and Why It's Your Best Friend
So, you understand the power of schema. But how do you implement it without needing a degree in computer science? Enter the hero of our story: the Schema Markup Generator.
A schema markup generator is an online tool designed to simplify the creation of structured data. Instead of manually writing lines of complex JSON-LD code, which is prone to syntax errors and can be time-consuming, you use a user-friendly interface. You simply select the type of schema you want (e.g., a "Local Business," an "Article," a "Product"), fill out a form with relevant details about your content, and the tool automatically churns out the correctly formatted JSON-LD code.
This generated code is then copied and pasted into your website’s HTML, usually in the <head> section, making the process accessible to virtually anyone, regardless of their coding background.
The core benefits of using a generator are undeniable:
- Time & Error Reduction: Generators automate code creation, saving you hours of manual coding. More importantly, they minimize syntax errors, which are common when coding by hand and can prevent your schema from being recognized by search engines.
- Accessibility for Non-Coders: This is perhaps the biggest win. Schema markup, once the domain of developers, is now a powerful SEO technique accessible to content creators, marketers, and small business owners who might not have any coding experience.
- Consistency and Best Practices: Reputable generators are built to adhere to Schema.org standards and Google's guidelines, helping you implement schema correctly from the start.
Navigating the Landscape: Common Schema Types You'll Use
Schema.org defines hundreds of schema types, but most websites will primarily use a handful of common ones. Generators typically support the most impactful and frequently used types. Understanding these will help you choose the right "index card" for your content.
Here are some of the most popular types supported by generators, along with key properties you'll likely fill out:
- Article: Ideal for blog posts, news articles, and informational pages.
- Properties: Headline, Author, Date Published, Image, Publisher (Organization/Person), Description, URL.
- LocalBusiness: Essential for any business with a physical location.
- Properties: Name, Address, Phone, Opening Hours, Price Range, GeoCoordinates, reviews, map location, URL, Logo, SameAs (social profiles).
- Product: For items you sell online. Critical for e-commerce.
- Properties: Name, Image, Description, Brand, SKU, Offers (Price, Currency, Availability), AggregateRating (star ratings), Reviews, MPN/GTIN.
- Event: Perfect for concerts, webinars, conferences, or any scheduled occurrence.
- Properties: Name, Start Date, End Date, Location, Offers (Ticket Price), Performer, Organizer, Description, Image.
- FAQPage: For pages dedicated to frequently asked questions and their answers. Creates expandable rich snippets.
- Properties: Question (text), AcceptedAnswer (text).
- HowTo: For step-by-step instructions (e.g., "How to bake a cake").
- Properties: Name, Step (name, text, image, duration), Total Time (ISO 8601 format), Tool, Supply.
- Recipe: Specifically for food preparation instructions.
- Properties: Name, Ingredients, Instructions, Cook Time, Prep Time, Total Time, Nutrition Information, Image, AggregateRating.
- Person: For individuals, such as authors, experts, or public figures.
- Properties: Name, Job Title, Affiliation, Alumni Of, WorksFor (Organization), SameAs (social profiles), Image, Description.
- Organization: For companies, NGOs, schools, or any type of organization. Often used site-wide.
- Properties: Name, Logo, URL, Address, Contact Point, founder, SameAs (social profiles), Tax ID/VAT ID, Legal Name, department, makesOffer, hasOfferCatalog.
- WebPage: Defines the main content of a webpage and its relationship to the overall website and organization. Useful for general site structure.
- Properties: URL, isPartOf (Website), mainEntity (the primary schema type on the page).
Choosing the correct schema type is the first and most critical decision. If you mark up a blog post as a "Product," Google will likely ignore it or, worse, potentially flag it as misleading.
Your Step-by-Step Masterclass: Using a Schema Markup Generator Like a Pro
Ready to supercharge your site's visibility? Let's walk through the process of using a schema markup generator from start to finish.
Step 1: Choosing Your Co-Pilot (The Generator)
The first step is to select a reliable online tool. Many free, reputable generators are available. For WordPress users, SEO plugins often include built-in schema generation features, which can be even more streamlined.
- Online Generators:
- Merkle's Schema Markup Generator: A very popular and user-friendly option, supporting a wide range of schema types.
- TechnicalSEO.com Schema Markup Generator: Another excellent choice, offering clear interfaces and robust options.
- RankRanger's Free Schema Markup Generator: Simple and effective for common types.
- CMS Plugins (for WordPress users):
- Yoast SEO: Offers integrated schema features, especially for Article, Organization, and Person schema.
- Rank Math: Known for its comprehensive schema module, allowing detailed configuration for many types.
- Advanced Tools: For those building complex knowledge graphs and assigning
@idproperties for interconnected entities, tools like Schemantra can be very useful.
For this guide, we'll assume you're using a free online generator, but the principles apply across the board.
Step 2: Identifying Your Page's Persona (Selecting Appropriate Schema Type)
Before you touch any generator, look at the specific webpage you want to optimize. What is its primary purpose?
- Is it a blog post? Choose
Article. - Is it a product page on your e-commerce site? Choose
Product. - Is it your business's contact page? Choose
LocalBusinessorOrganization. - Does it list FAQs? Choose
FAQPage.
Crucially, choose the type that most accurately describes the main content of that specific web page. Don't try to fit a square peg into a round hole.
Step 3: Feeding the Machine (Accurate Data Entry)
Once you've selected your schema type in the generator, you'll see a series of fields to fill out. This is where precision is key.
- Match Visible Content: The golden rule of schema is that the information in your structured data must accurately reflect the content visible on your webpage. Don't mark up hidden content or information that isn't present for users to see. This is a common pitfall that can lead to Google ignoring your schema or even issuing a manual penalty.
- Completeness: Fill in as many relevant fields as possible, especially the required ones. The more complete and accurate your schema, the better search engines can understand your content. For example, for a
Productschema, ensure you include the product's name, description, image, price, currency, and availability. - Specific Formats: Pay attention to any specific format requirements, such as ISO 8601 for dates and times (
YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SSZ) or valid URLs.
Step 4: The Magic Happens (Generating the Code)
After meticulously filling out all the fields, you'll typically find a button labeled something like "Generate Schema," "Create Code," or "Get JSON-LD." Click it, and watch as the generator instantly produces a block of code on the side or in a dedicated window.
Step 5: Copy-Paste Perfection (Grabbing Your JSON-LD)
The generator will output a block of JSON-LD code, usually enclosed within <script type="application/ld+json"> tags. This is your schema markup.
Copy the entire code block. Make sure you include the opening and closing script tags, as these are essential for the browser and search engines to interpret the code correctly.
Step 6: Bringing It Home (Implementing on Your Website)
This is where you integrate the generated code into your website. There are several ways to do this, depending on your website's setup:
- Direct HTML Insertion (Recommended for Most): The most common and often recommended method is to paste the code into the
<head>section of your page's HTML. Placing it here ensures it's loaded early, though<body>or<footer>also technically work. - If you have direct access to your theme files, you might find a
header.phpfile (for WordPress) or a similar template where you can insert the code. - WordPress Specific Methods:
- Theme Options: Many modern WordPress themes include a dedicated "Header Scripts" or "Custom Code" section in their theme options, allowing you to paste code directly into the
<head>or<body>. - Header/Footer Plugins: Plugins like "Head, Footer and Post Injections" or "Insert Headers and Footers" provide an easy interface to paste code without touching theme files.
- Custom HTML Blocks/Widgets: For specific page types, some page builders or themes allow adding custom HTML blocks where you can paste the schema.
- SEO Plugins (Yoast/Rank Math): As mentioned, these plugins often have their own schema generation and implementation, which is usually the cleanest method if you're using them. They handle the placement automatically when you configure schema through their settings.
- Google Tag Manager (GTM): For more advanced users, agencies, or websites with complex tracking, GTM is an excellent way to deploy schema markup.
- Create a new Custom HTML tag in GTM.
- Paste your entire JSON-LD code block into the HTML field.
- Set the trigger to fire on "Page View" for the specific page(s) where you want the schema to appear. GTM will inject the schema into the page at runtime.
No matter your method, ensure the code is present on the correct page and is not causing any visible disruption to your site's layout or functionality.
The Non-Negotiable Step: Validating Your Schema Markup
Generating and implementing schema is only half the battle. You absolutely must validate your markup to ensure it's correctly structured, free of errors, and eligible for rich results. Skipping this step is one of the most common reasons schema fails to appear in search.
Here are the essential tools:
- Google's Rich Results Test (Essential for Rich Snippets):
- Purpose: This is your primary tool for checking if your page's structured data is valid and eligible for rich results on Google Search. It simulates how Google sees your page and tells you exactly which rich results (e.g., product snippets, event listings) your schema qualifies for.
- How to Use: Go to Google's Rich Results Test, enter your page's URL or paste the code directly, and run the test.
- What to Look For: Green checkmarks indicating "Valid item detected" and a list of detected rich results. If there are errors or warnings, address them immediately.
- Schema Markup Validator (Schema.org) (For Comprehensive Syntax):
- Purpose: This tool, provided by Schema.org, offers a more technical, comprehensive syntax validation for any structured data adhering to the Schema.org vocabulary. It's excellent for debugging precise structural issues.
- How to Use: Visit Schema.org's Markup Validator, enter your URL or code.
- What to Look For: Detailed reports on all detected entities, properties, and any syntax errors or warnings that might cause issues.
- Classy Schema Structured Data Viewer (For Visualizing Your Knowledge Graph):
- Purpose: This lesser-known but incredibly useful tool helps you visualize your structured data as a graph. It's fantastic for understanding how your entities relate to each other, ensuring you're building a coherent "knowledge graph" that AI systems can easily interpret.
- How to Use: Go to Classy Schema, enter your URL.
- What to Look For: A clear, interconnected diagram of your schema. This helps you spot if entities are properly linked or if something is missing.
Correcting Errors: If any validation tool flags errors, go back to your generator (or direct code) and make the necessary corrections. Common fixes include ensuring all required fields are populated, URLs are absolute, dates are in the correct format, or nested items are properly closed. ChatGPT can even assist in quickly fixing syntax errors if you paste the problematic JSON-LD and ask it to debug.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Schema Strategies
Once you're comfortable with the fundamentals, consider these advanced techniques to maximize your schema's impact:
- Nesting Schema for Richer Context: Don't just implement one schema type in isolation. Nest related schema types within each other to create a more comprehensive and interconnected data structure.
- Example: A
Productschema can (and should) include a nestedAggregateRating(for overall star ratings) and individualReviewschemas. ALocalBusinesscan nestOpeningHoursSpecificationandGeoCoordinates. This creates a richer, more descriptive data set that search engines love. - Multiple Schema Types on a Single Page: If a single page legitimately covers different primary entities, you can (and sometimes should) implement multiple, distinct JSON-LD blocks.
- Example: A conference page might feature an
Eventschema for the conference itself,Personschemas for individual speakers, and anOrganizationschema for the host. Each block should clearly describe its respective entity. - Dynamic Data Integration for Large Websites: For large e-commerce sites, news portals, or directories with thousands of pages, manually generating schema is impractical. Explore programmatic solutions where your CMS or backend system automatically generates JSON-LD from database information (e.g., product details, article metadata) as pages are rendered. This ensures scalability and consistency.
- Target Specific Rich Results: Google's Search Gallery is a treasure trove. Visit it to identify the specific schema types and properties that power the rich results most relevant to your business goals. For instance, if you're an e-commerce store, prioritize
Product,Offer, andReviewschema to get those coveted shopping features.
Landmines to Avoid: Common Schema Markup Mistakes
Even with generators, it's easy to stumble. Be aware of these common pitfalls:
- Using the Wrong Schema Type: This is the most fundamental error. Marking up a "How-To" guide as a "Recipe" simply because it has steps will lead to ignored or misinterpreted schema. Always match the primary content type accurately.
- Incomplete or Inaccurate Information: As mentioned, data in your schema must precisely match the visible content on your webpage. Don't use placeholders, misleading information, or data that's out of date. Google's quality guidelines are strict on this.
- Forgetting Implementation: Generating the code is only step one. Many users forget to correctly place the code on their live website, rendering their efforts useless.
- Incorrect Placement or Syntax Errors: While generators reduce syntax errors, improper placement within your HTML or manual edits that introduce errors can still cause your schema to fail. Always use a validator.
- Not Validating Your Markup: This is critical! Skipping validation leaves your implementation unchecked. You might think your schema is working, but without validation, it could be riddled with errors that prevent rich snippets from appearing or even lead to manual actions (penalties) if you're inadvertently violating guidelines.
- Violating Google Guidelines: Beyond accuracy, avoid using schema to mark up hidden content (e.g., text hidden behind a tab that's not easily accessible to users), irrelevant information, or content intended to manipulate search rankings. Google's structured data policies are designed to prevent abuse.
- Inconsistent Use: For large websites or teams, decide on a primary method (e.g., a specific online generator, a particular SEO plugin) and stick to it. Inconsistent application can lead to fragmented schema or conflicts that are hard to troubleshoot.
Schema FAQs: Quick Answers to Your Burning Questions
You've got questions; we've got quick answers.
Q: Does schema markup guarantee rich snippets?
A: No, schema markup makes your content eligible for rich snippets, but Google ultimately decides whether to display them. Factors like content quality, search query relevance, and overall site authority also play a role. However, without correct schema, eligibility is impossible.
Q: Can I use multiple schema types on one page?
A: Yes, absolutely! If a single page covers different entities (e.g., a product review page with both Product and Review schema, or an article about an Event with Person schemas for speakers), you should implement multiple, distinct JSON-LD blocks for each relevant schema type.
Q: Is schema a ranking factor?
A: Directly, Google states that structured data is not a direct ranking factor. However, indirectly, it's a huge factor. Rich snippets lead to higher CTR, which can signal to Google that your content is more relevant and valuable, potentially improving rankings over time. More importantly, it helps Google understand your content, which is foundational to ranking effectively.
Q: How often should I update my schema?
A: You should update your schema whenever the underlying content on your page changes significantly. If a product's price or availability changes, if an event date shifts, or if an article is substantially revised, update the corresponding schema markup to ensure accuracy.
Your Journey Forward: Continuous Optimization
Mastering a schema markup generator empowers you to speak Google's language, enhancing your website's visibility and user experience. But the journey doesn't end with implementation.
- Monitor Performance in Google Search Console (GSC): This is your feedback loop. Regularly check the "Enhancements" reports in GSC. You'll find specific reports for various rich result types (e.g., Products, Reviews, FAQs). These reports will show you how many pages Google has detected with valid structured data, identify any errors or warnings, and help you track your rich result performance.
- Stay Updated: The web is constantly evolving. Keep an eye on Schema.org updates and Google's structured data guidelines. As AI advancements continue, the importance and complexity of structured data will only grow.
By embracing structured data and leveraging the power of schema markup generators, you're not just optimizing for today's search engines; you're building a more understandable, clickable, and future-proof presence on the web. It's a strategic investment that pays dividends in visibility, engagement, and authority. Now go forth and generate schema markup that makes your content sing!